목록graph deep learning (15)
yuns
Four Limitations Computationally inefficient to update the hidden states of nodes iteratively to get the fixed point. uses the same parameters in the iteration while most opoular neural networks use different parameters in different layers, which serves as a hierarchical feature extraction method some informative edges(Knowledge Graph) cannot be effectively modeled in GNN. if T is pretty large, ..
 4.2 Model
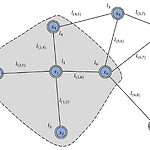
4.2 Model
hv=f(xv,xco[v],hne[v],xne[v]) ov=g(hv,xv) Functions f: local transition function which is shared among all nodes g : local output function Symbols x: the input feature h: hidden state co[v]: the set of edges connected to node v ne[v]: the set of neighbors of node v xv: the features of v xco[v]: the features of its edges hne[v]: the states..
ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/4700287/ [IEEE 09] The Graph Neural Network Model 작성 기준 1624회 인용 The Graph Neural Network Model - IEEE Journals & Magazine ieeexplore.ieee.org Node는 각각의 feature들과 연결되어 있는 node들로 표현된다. GNN의 target to learn a state embedding hv∈Rs encodes the information of the neighborhood 이웃들의 정보를 encoding hv는 output인 ov을 만들어내기 위해 사용됨 논문에서 "Undirected ..
 GNN소개 및 내용 정리
GNN소개 및 내용 정리
참조: (번역) medium.com/watcha/gnn-%EC%86%8C%EA%B0%9C-%EA%B8%B0%EC%B4%88%EB%B6%80%ED%84%B0-%EB%85%BC%EB%AC%B8%EA%B9%8C%EC%A7%80-96567b783479 GNN 소개 — 기초부터 논문까지 이 글은 Shanon Hong의 An Introduction to Graph Neural Network(GNN) For Analysing Structured Data를 저자에게 허락받고 번역, 각색한 글이다. medium.com 참조: (원본) towardsdatascience.com/an-introduction-to-graph-neural-network-gnn-for-analysing-structured-data-afce79f4..
an algorithm based on gradient descend to optimize the parameters in a model. 3.3 Neural Networks Feedforward neural network Convolutional neural network Recurrent neural network Graph neural network
2.2.1 Basic Concepts and Formulas Random variable a variable that has a random value. X로부터 x1와 x2의 두 변수가 나올 수 있게 될 경우 아래의 식이 성립한다. P(X=x1)+P(X=x2)=1] Joint probability 두 개의 random variable X, Y에서 각각 x1와 y1가 뽑힐 확률 P(X=x1,Y=y1) Conditional Probability Y=y1가 뽑혔을 때 X=x1가 같이 뽑힐 확률 P(X=x1|Y=y1) fundamental rules sum rule: P(X=x)=∑yP(X=x,Y=y) product rule: $P(..
 2.1 Linear Algebra
2.1 Linear Algebra
2.1.1 Basic Concepts Scalar: A number Vector: A column of ordered numbers x=[x1x2⋮xn] norm of vector: the length Lp norm: ||x||p=(∑ni=1|xi|p)1/p L1 norm: ||x||1=(∑ni=1|xi|) L2 norm: ||x||2=√∑ni=1xi2 --> used to measure the length of vectors L∞ norm: $||x||_\infty = max_i..
