yuns
Lecture 3 Motifs and Structural Roles in Networks 본문
Lecture 3 Motifs and Structural Roles in Networks
yuuuun 2020. 12. 20. 18:10z-score: z = $X-\mu / \sigma$로 계산하여 표본이 평균으로부터 몇 구간의 표준편차만큼 떨어져 있는지 알려주는 값
Motifs and Structural Roles in Networks
SubNetworks (subgraphs)
- 네트워크의 부분집합
- charaterize와 discriminate 가능
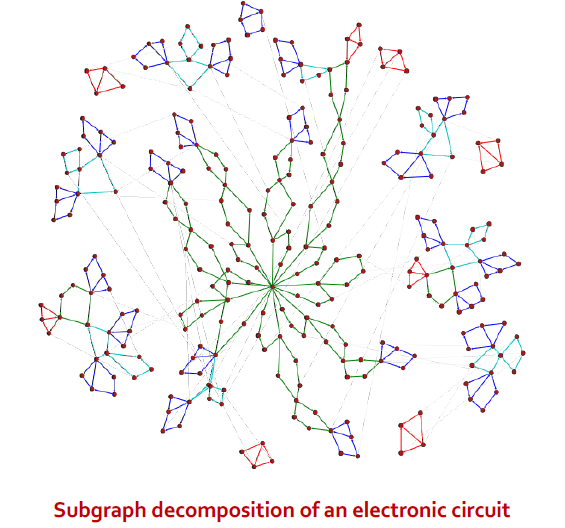
Case Example of SubGraphs
방향 그래프에서 나올 수 있는 모든 가능한 subgraph들
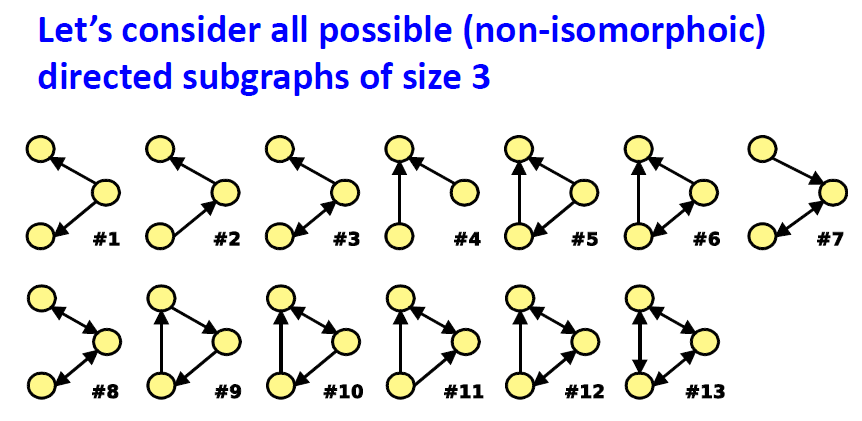
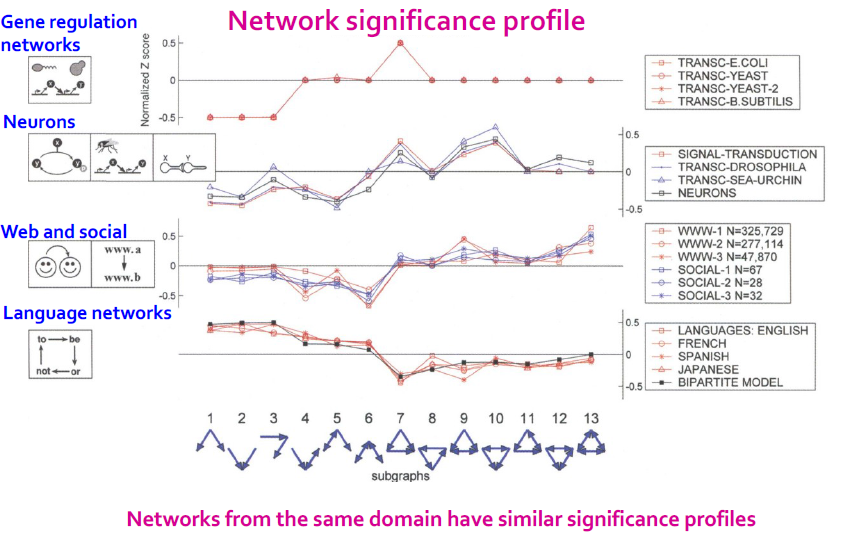
- subgraph "significance"를 분류 가능한 metric 고려
- Negative value: Under-representation
- Posivite value: Over-representation
- Network significance profile
- feature vector with values for all subgraph types
- Diverse domain
- Regulatory network(gene regulation)
- Neuronal network(synaptic connections)
- World Wide Web(hyperlinks between pages)
- Social Network(Friendships)
- Language networks(word adjacency)
Subgraphs, Motifs, and Graphlets
Network Motifs
반복적이고 중요한 interconnection 연결 패턴(recurring, significant patterns of interconnections)
큰 그래프에서 반복적이고 통계적으로 중요한 subgraph들 (다양한 네트워크간에 반복되는 subgraph)
Network Motif를 정의하는 방법
- Pattern: subgraph에서 발생함
- Recurring: 많이 발생함
- Significant: 랜덤으로 생성해낸 network보다 더 자주 발생함
Why do we need motifs?
Motifs
- network가 어떤식으로 동작하는지 알려줌
- 주어진 상황에서 network의 operation과 reaction을 예측하는데 도움줌
Examples
- Feed-forward loops: network의 neruon에서 발견되며 'biological noise'을 중화
- Parralel loops: food web에서 사용(먹이사슬)
- Single-input modules: gene control network에서 사용
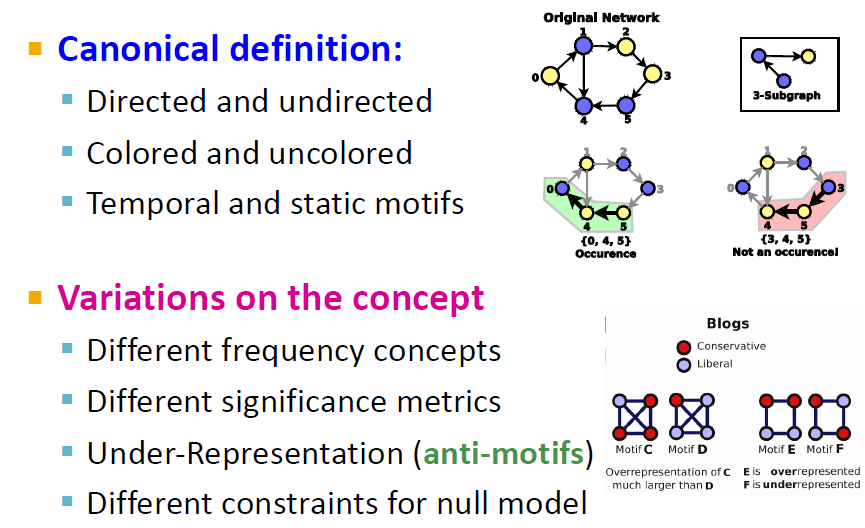
Induced Subgraphs
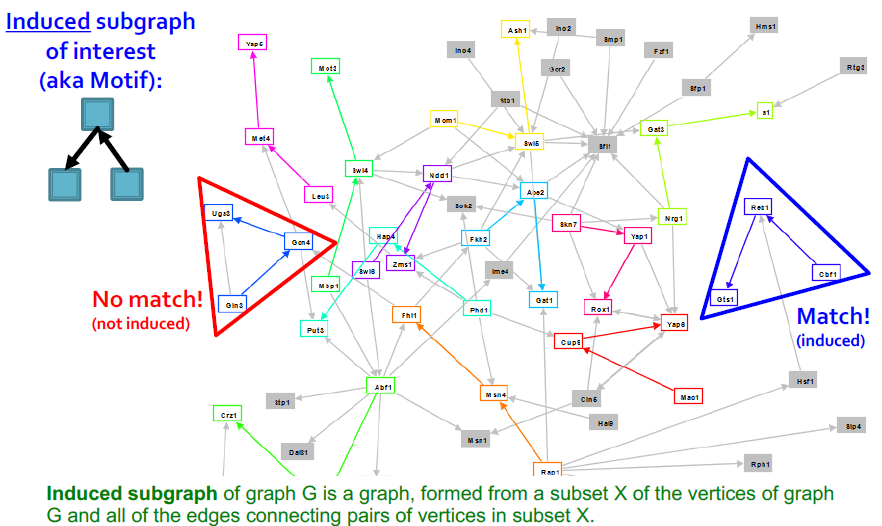
빨간색 subgraph의 경우에는, edge가 하나 더 존재하기 때문에 해당되지 않음(정확히 똑같을 것)
Recurrence
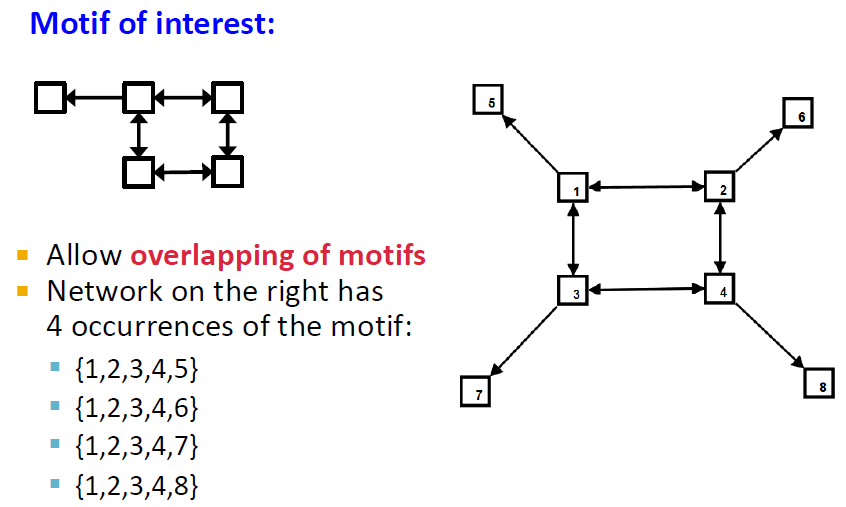
4개의 motif가 존재함
정확히 같지는 않은 아이들
Significance of a Motif
실제로 더 많이 생성되는 network들이 random network보다 functional significance가 높음. 즉, motif의 경우, 무작위로 생성된 그래프보다 실제 네트워크에서 더 잘 표현이 됨. Overrepresented
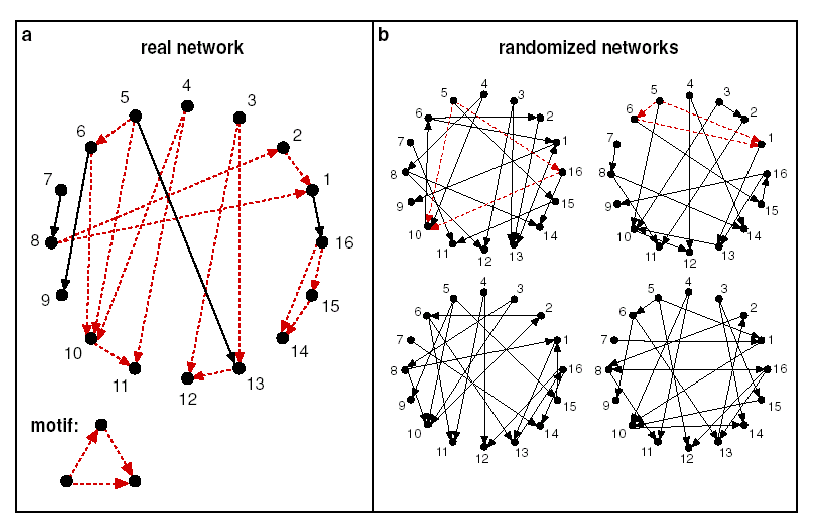
- Z-score를 통하여 통계적인 significance를 지표화하여 motif 계산 가능

$G^{rand}$을 generate해야 하는데 이 때 사용하는 model은 configuration model
- Network Significance Profile(SP)
- Z-score를 normalize하는 값 $$SP_i = \frac{Z_i}{\sqrt{\sum_j Z_j^2}}$$
- subgraph의 상대적인 significance를 강조할 때 사용하기 위함
Z-score를 비교하기 위하여, Random Graph를 생성해야 함!
Configuration Model
주어진 degree sequence $k_1, k_2, \cdots, k_N$을 이용하여 random graph를 생성하기 위함
실제 그래프 $G^{real}$와 random 그래프 $G^{rand}$는 같은 차수의 Sequence를 가지고 있음
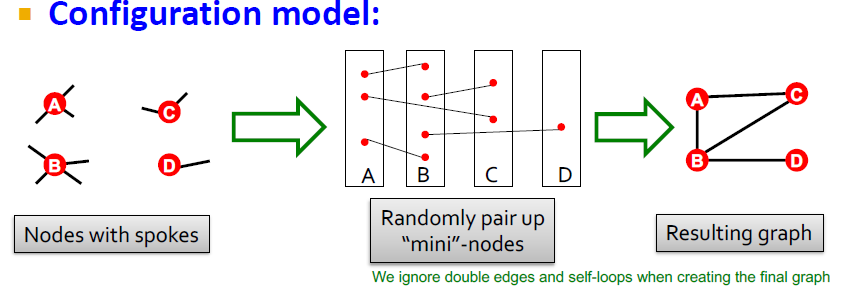
각 node당 degree가 정해져 있으면 이를 랜덤하게 pair up할 것인데, 실제로 그래프가 만들어진 것을 보면 degree가 맞지 않는 문제가 발생하는 것을 확인할 수 있음(approximate degree sequence)
Alternative for Spokes: Switching
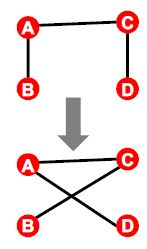
- 주어진 그래프 G에서 switching step인 $Q\times |E|$번 아래의 단계를 반복
- edge의 pair를 선택하여 cross시켜서 바꾸기
- 교체할 때, 자신을 가리키거나 두 node간 edge가 여러개일 경우에는 발생하지 않음
- edge의 pair를 선택하여 cross시켜서 바꾸기
- 결과: randomly rewired graph
- same node degrees, randomly rewired edges
- Q가 충분히 크게 되면, converge할 것
Detecting Motifs
- $G^{real}$에서 subgraph인 $i$
- $G^{rand}$에서 subgraph인 $i$
- $G^{rand}는 $G^{real}$와 똑같은 수의 node, edge, degree distribution을 가지고 있음
- i에 대한 Z-score $$Z_i = \frac{(N_i^{real} - \bar{N}_i^{rand})}{std(N_i^{rand})}$$
- Z-score가 높을 수록 subgraph $i$는 network G의 motif을 잘 나타냄
Variations on the Motif Concept
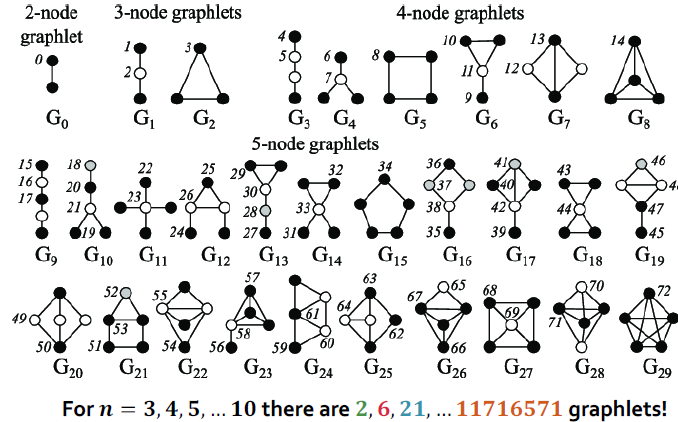
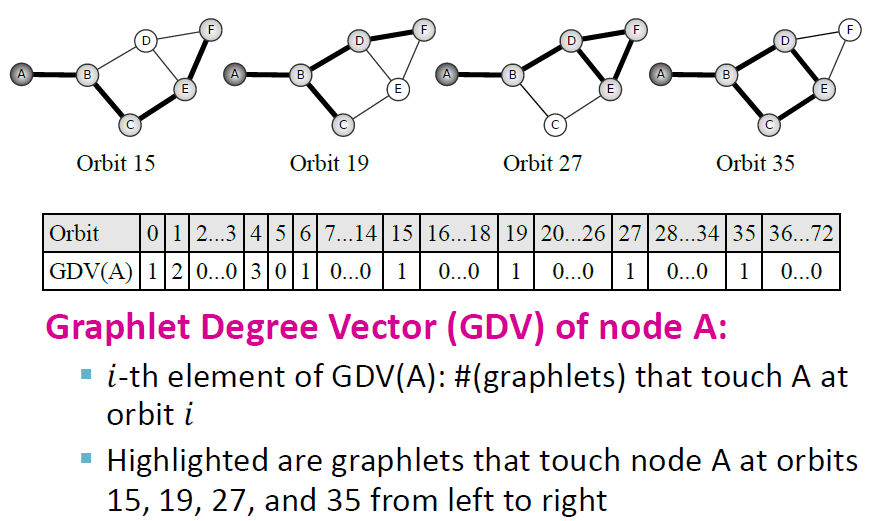
Graphlets: Node feature vectors
Graphlets: 연결된 비동형 subgraph
Graphlet Degree Vector
- node-level subgraph metric(평가지표)를 알기 위하여 graphlet 사용
- degree는 node와 연결되어 있는 edge의 개수를 의미
- Graphlet degree vector는 node와 연결되어 있는 "graphlet의 개수"
Automorphism Orbits
- 그래프의 symmetry도 고려해줌
- GDV: 각 orbit position에서 vector의 frequency를 가지는 vector
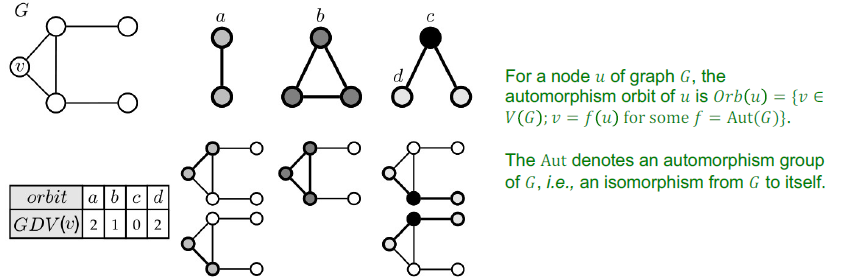
Graphlet Degree Vector(GDV)
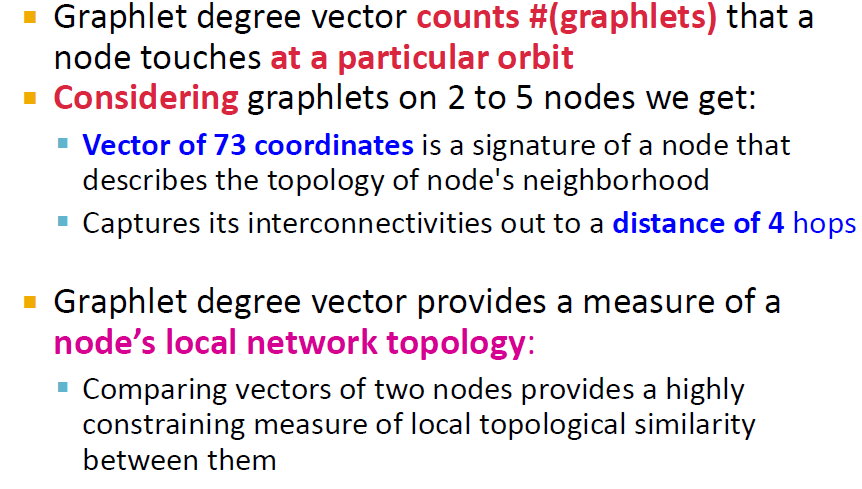
Example
Finding Motifs and Graphlets
2 challenges of finding size-k motifs/graphlets
- Enumerating: 모든 k 크기의 부분 그래프를 발생시키기
- Counting: 서브그래프의 개수를 세는 NP-complete problem
Counting Subgraphs
Algorithm
- Exact subgraph enumeration(ESU)
- Kavosh
- Subgraph sampling
Exact subgraph enumeration(ESU)
두개의 set를 가지는 recursive algorithm
- $V_{subgraph}$: currently constructed subgraph(motif)
- $V_{extension}$: set of candidate nodes to extend the motif
Idea
- node $v$에서 시작하여 다른 node $u$를 $V_{extension}$에 아래의 조건이 부합할 경우 추가
- $u$의 node_id가 $v$보다 클 것
- $u$가 이미 $V_{subgraph}$에 포함되어 있는 노드가 아닐 경우, 그와 연결된 node임
ESU는 recursive funtion
- tree구조를 하고 있기 때문에 ESU-Tree라고도 함
Algorithm

ESU-Tree Example
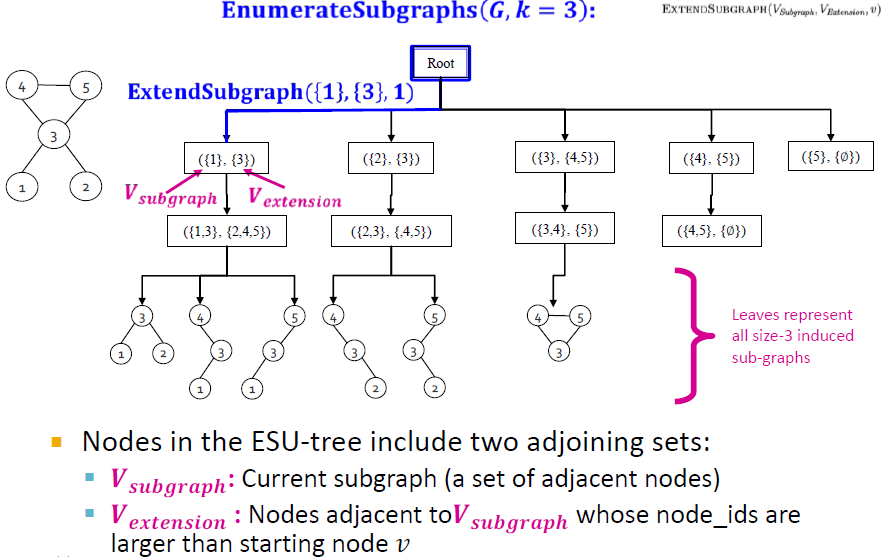
깊이가 k=3인 ESU-Tree
- 첫번째 단계에서 $V_{subgraph}$은 시작노드들로 구성되어 있고, $V_{extension}$는 해당 노드들과 연결되어 있는 $V_{subgraph}$보다 큰 node들이 추가되어 있음을 확인할 수 있다.
- 두 번째 단계에선 첫번째 단계에 있던 $V_{extension}$에 해당하는 값을 $V_{subgraph}$에 넣어주고 $V_{subgraph}$과 연결되어 있는 노드들을 입력해준다.
Use ESU-Tree to Count Subgraphs
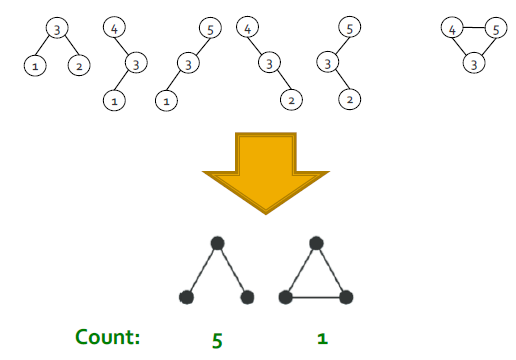
ESU-Tree에 배치된 subgraph를 topologically equivalent(=isomorphic)으로 분류하고 그에 따라 subgraph 클래스로 그룹화하고 McKay의 nauty algorithm을 사용한다.
(subgraph의 개수를 구할 때는 위상학적으로 같은지 판별하는 과정에서 nauty algorithm을 사용)
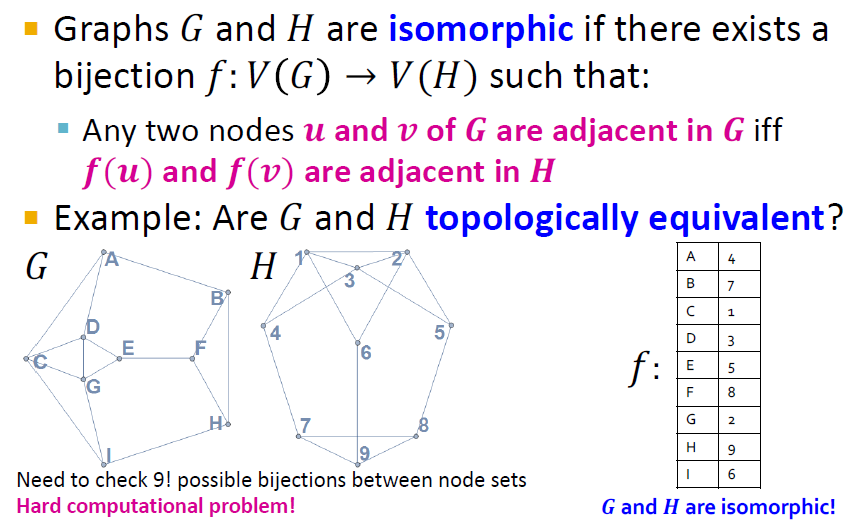
Graph Isomorphism
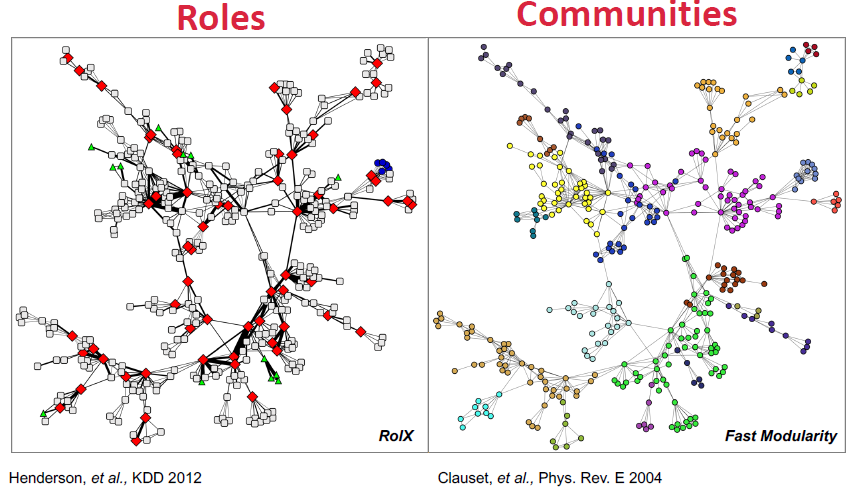
Structural Roles in Networks
Role이란, network에서의 node들의 "function"을 의미함
Roles vs Groups in Networks
- Role: network에서 유사한 위치를 가지는 node들의 collection
- Role는 node의 subset간의 similarity을 기반으로 함
- Group는 adjacency, proximity, reachability에 의해 형성되기 때문에 role과 는 다름
동일한 역할을 가지 node는 서로 직간접적으로 상호작용할 필요가 없음
- Role: 유사한 structural property를 가지는 node들의 집합
- Communities/Groups: 서로 잘 연결되어 있는 node들의 집합
- Role과 community들은 서로 상호 보완적임
- 예시
- Role: Faculty, Staff, Students
- Communities: AI Lab, Info Lab, Theory Lab
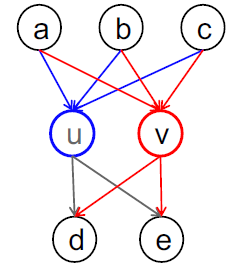
Roles: More Formally
- Strucural equivalence
- Node $u, v$가 다른 노드들에 대하여 같은 relationship을 가지고 있을 경우, 구조적으로 동일하다.
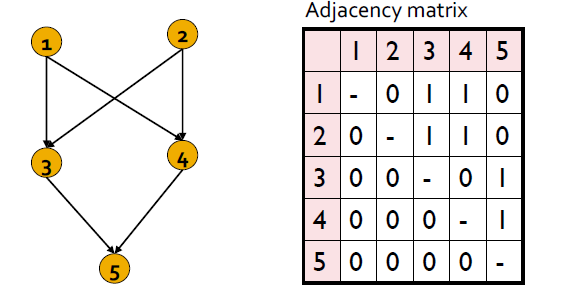
Discovering Structural Roles in Networks
Role이 중요한 이유
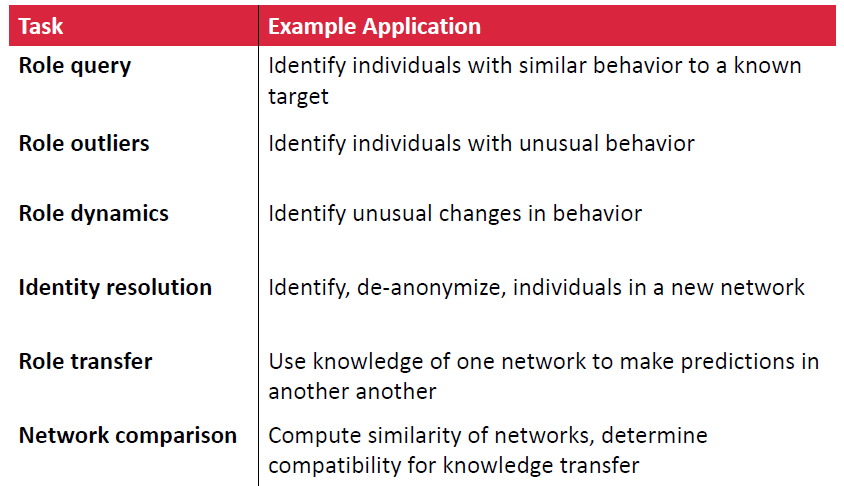
Structural Role Discovery Method
RoIX: 네트워크의 구조적인 role을 자동적으로 찾을 수 있도록 함
- 비지도 학습, 불필요한 선행 정보, 각 node에 roles에 혼합된 역할 할당, edges들의 갯수에 선형적
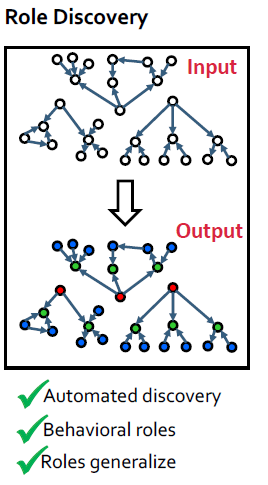
Approach Overview
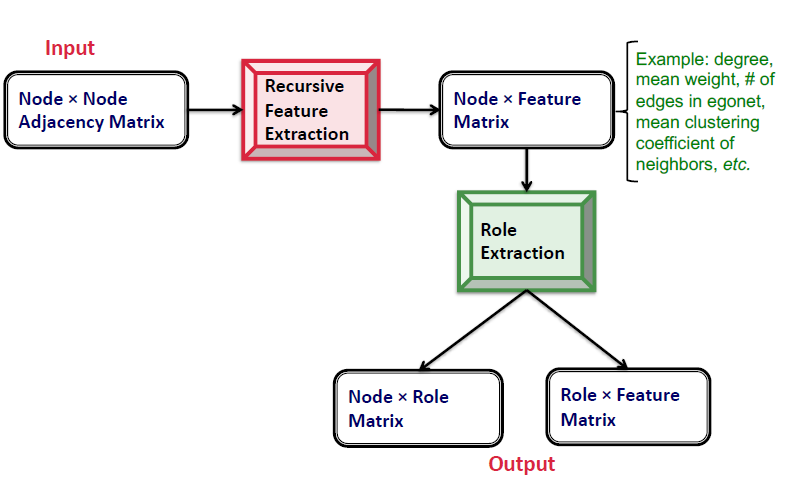
- Input: Node $\times$ Node Adjacency Matrix
- Recursive Feature Extraction을 통하여 Node $\times$ Feature Matrix 생성
- Role Extraction을 통하여 1) Node $\times$ Role Matrix와 2) Role $\times$ Feature Matrix 생성
Recursive Feature Extraction
network connectivity를 구조적인 feature로 전환하기 위한 방법이다.
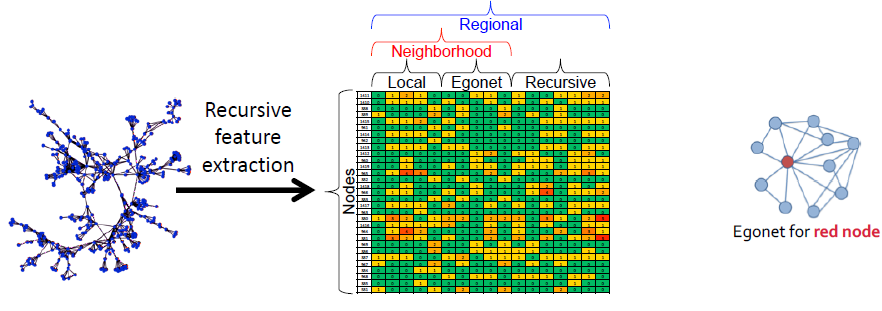
KEY IDEA: node의 feature을 aggregate하고 새로운 recursive feature를 생성하는데 사용하는 것
- Local Features: node degree의 전체 척도
- directed network의 경우, in-, out- degree와 total degree를 포함
- weighted network의 경우, weighted feature version 포함
- Egonet Features: node의 주위 정보 이용
- 노드와 자신들의 이웃, induced subgraph의 정보 이용
Recursive Feature Extraction
- node feature의 base set로부터 시작하여 아래 feature를 생성하기 위하여 current node feature의 집합을 사용
- 2가지 agrregate function: mean, sum
- 예) 이웃한 node 사이의 "unweighted degree" feature의 평균값을 새로운 feature로 추가
- 2가지 agrregate function: mean, sum
- Pruning Technique: 재귀적으로 반복될 경우, 가능한 recursive feature들의 개수가 지수적으로 증가하기 때문에
Role Extraction
Extract된 node의 feature들을 이용하여 node를 clustering
Application: Structural Similarity
Task: Structural Similarity을 기반으로 한 node의 clustering
Role distribution을 비교하여 구조적인 유사도를 비교가능

'[CS224W] Machine Learning with Graphs' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2020-01 Intro (0) | 2021.06.14 |
|---|---|
| Lecture 3 Motifs and Structural Roles in Networks (0) | 2020.12.29 |
| Chapter 2 Properties of Networks, Random Graph Models (0) | 2020.12.19 |
| Lecture 1 Introduction - Structure of Graphs (0) | 2020.12.19 |




